What are multilayer perceptrons?
The perceptron is very useful for classifying data sets that are linearly separable. They encounter serious limitations with data sets that do not conform to this pattern as discovered with the XOR problem. The XOR problem shows that for any classification of four points that there exists a set that are not linearly separable.

The MultiLayer Perceptron (MLPs) breaks this restriction and classifies datasets which are not linearly separable. They do this by using a more robust and complex architecture to learn regression and classification models for difficult datasets.
How does a multilayer perceptron work?
The Perceptron consists of an input layer and an output layer which are fully connected. MLPs have the same input and output layers but may have multiple hidden layers in between the aforementioned layers, as seen below.
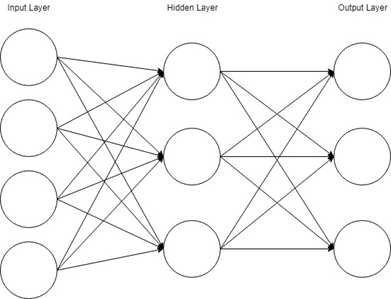
The algorithm for the MLP is as follows:
Just as with the perceptron, the inputs are pushed forward through the MLP by taking the dot product of the input with the weights that exist between the input layer and the hidden layer (WH). This dot product yields a value at the hidden layer. We do not push this value forward as we would with a perceptron though.
MLPs utilize activation functions at each of their calculated layers. There are many activation functions to discuss: rectified linear units (ReLU), sigmoid function, tanh. Push the calculated output at the current layer through any of these activation functions.
Once the calculated output at the hidden layer has been pushed through the activation function, push it to the next layer in the MLP by taking the dot product with the corresponding weights.
Repeat steps two and three until the output layer is reached.
At the output layer, the calculations will either be used for a backpropagation algorithm that corresponds to the activation function that was selected for the MLP (in the case of training) or a decision will be made based on the output (in the case of testing).
MLPs form the basis for all neural networks and have greatly improved the power of computers when applied to classification and regression problems. Computers are no longer limited by XOR cases and can learn rich and complex models thanks to the multilayer perceptron.
